

The Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances (NDPS) Act was enacted to control and regulate narcotic drugs. Read here to know the details of the act.
A Bill to replace an ordinance amending the Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances (NDPS) Act, 1985 was introduced in the Lok Sabha and passed on December 13. Rajya Sabha passed Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances (Amendment) Bill, 2021. The Bill was introduced by the Union Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman to amend the Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances Act, 1985 aiming to correct a drafting error created by a 2014 amendment to the original legislation.
Table of Contents
“The Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances Act, 1985 (the NDPS Act) was enacted to consolidate and amend the law relating to narcotic drugs, to make stringent provisions for the control and regulation of operation relating to narcotic drugs and psychotropic substances, to provide for the forfeiture of property derived from, or used in, illicit traffic in narcotic drugs and psychotropic substances and to implement the provisions of the International Convention on Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances and for matters connected therewith.”
The Act regulated operations like manufacture, transport, and consumption of narcotic drugs and psychotropic substances.
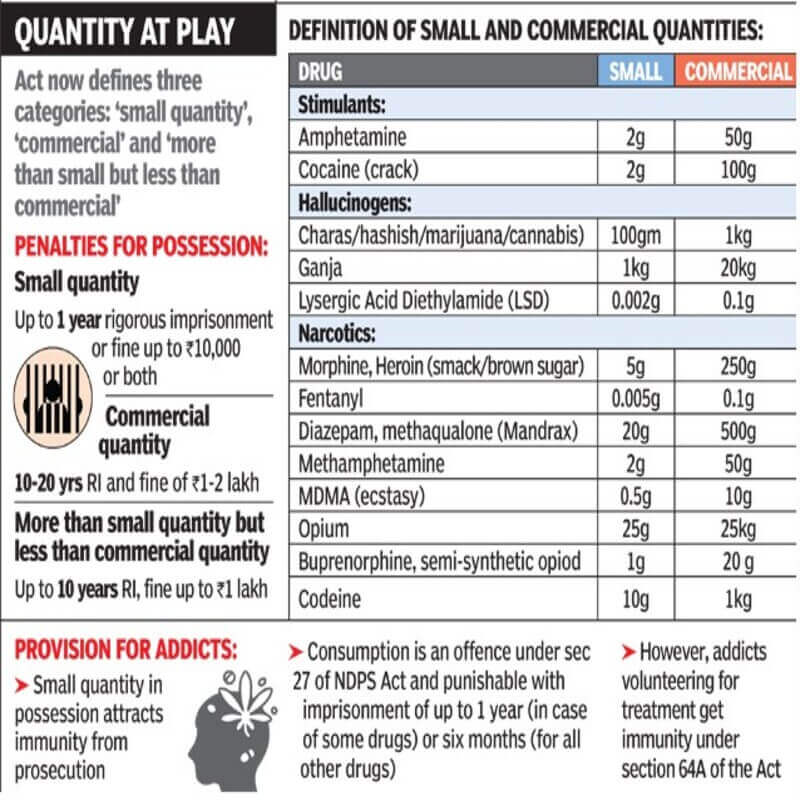
Under the Act, financing certain illicit activities like cultivating cannabis, manufacturing narcotic drugs, or harbouring persons engaged in them is an offence.
Persons found guilty of this offence will be punished with rigorous imprisonment of at least 10 years, extendable up to 20 years, and a fine of at least Rs.1 lakh. It also provides for forfeiture of property derived from or used in, illicit traffic in narcotic drugs and psychotropic substances. It also provides for the death penalty in some cases where a person is a repeat offender.
The NDPS Act has since been amended thrice – in 1988, 2001, and 2014. The Act extends to the whole of India and it applies also to all Indian citizens outside India and to all persons on ships and aircraft registered in India.
👉 Which year are YOU targeting for success in the IAS/IPS/IFS Exam? 🚀
The Narcotics Control Bureau (NCB) was constituted in 1986 under the Act.
1989: NDPS Act amended with strict provisions with sections added including under section 27A for financing illicit traffic.
Illicit traffic means production, possession, sale, purchase, transportation, warehousing, user booked under Section 27A.
2001: Act amended to rationalize sentencing. The act was now easy on addicts and the bail was also liberalized.
2014: A substantial amendment was made to the NDPS Act to allow for better medical access to narcotic drugs. It defined “essential drugs”; under Section 9 and allowed the manufacture, possession, transport, import inter-State, export inter-State, sale, purchase, consumption, and use of essential narcotic drugs.
The NDPS (Amendment) Bill, 2021 would replace an ordinance promulgated in September to correct a drafting error in a 2014 amendment to the Act.
The anomaly crept in when the Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances (NDPS) Act was amended in 2014 to allow better medical access to narcotic drugs, removing state barriers in transporting and licensing of “essential narcotic drugs”.
Before the 2014 amendment, clause (viii-a) of Section 2 contained sub-clauses (i) to (v), which defined the term “illicit traffic”. This clause was re-lettered as clause (viii-b) by the Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances (Amendment) Act, 2014, as a new clause (viii-a) in section 2 defining ‘essential narcotic drugs’ was inserted. However, inadvertently consequential change was not carried out in section 27A of the NDPS Act.
The provision reads that whoever indulges in the financing, directly or indirectly, any of the activities specified in sub-clauses (i) to (v) of clause (viii-a) of section 2 or harbors any person engaged in any of the aforementioned activities. He shall be punishable with rigorous imprisonment for a term which shall not be less than ten years but which may extend to twenty years and shall also be liable to fine which shall not be less than one lakh rupees but which may extend to two lakh rupees:
Section 27A became inoperable because:
Few experts have observed that the Bill violated the fundamental rights of a citizen as it provides retrospective effect to offences starting in 2014.
It also violates the fundamental rights in Article 21 because you can be punished for an offence for which there is a law in existence at the time of the commission of the offence.